
The Food Safety Research of Animal Origin team of SHVRI, CAAS has developed a rapid and multi-target detection system, pioneeringly combining "one-step reaction in one-tube" sample preparation with microfluidic visualization analysis. The related research has been published in Food Control.
Background
Foodborne pathogens, notably Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella Enteritidis, and Staphylococcus aureus , pose a significant threat to human life and health globally, causing numerous illnesses annually. Furthermore, due to the abundance of nutrients and conducive environment for microbial growth, food contamination often involves the simultaneous presence of these three types of pathogens. Therefore, early and multi-target detection of these pathogens in food is crucial to mitigate However, traditional methods are typically time-consuming, labor-intensive, and costly, limiting their practical application.
Progress
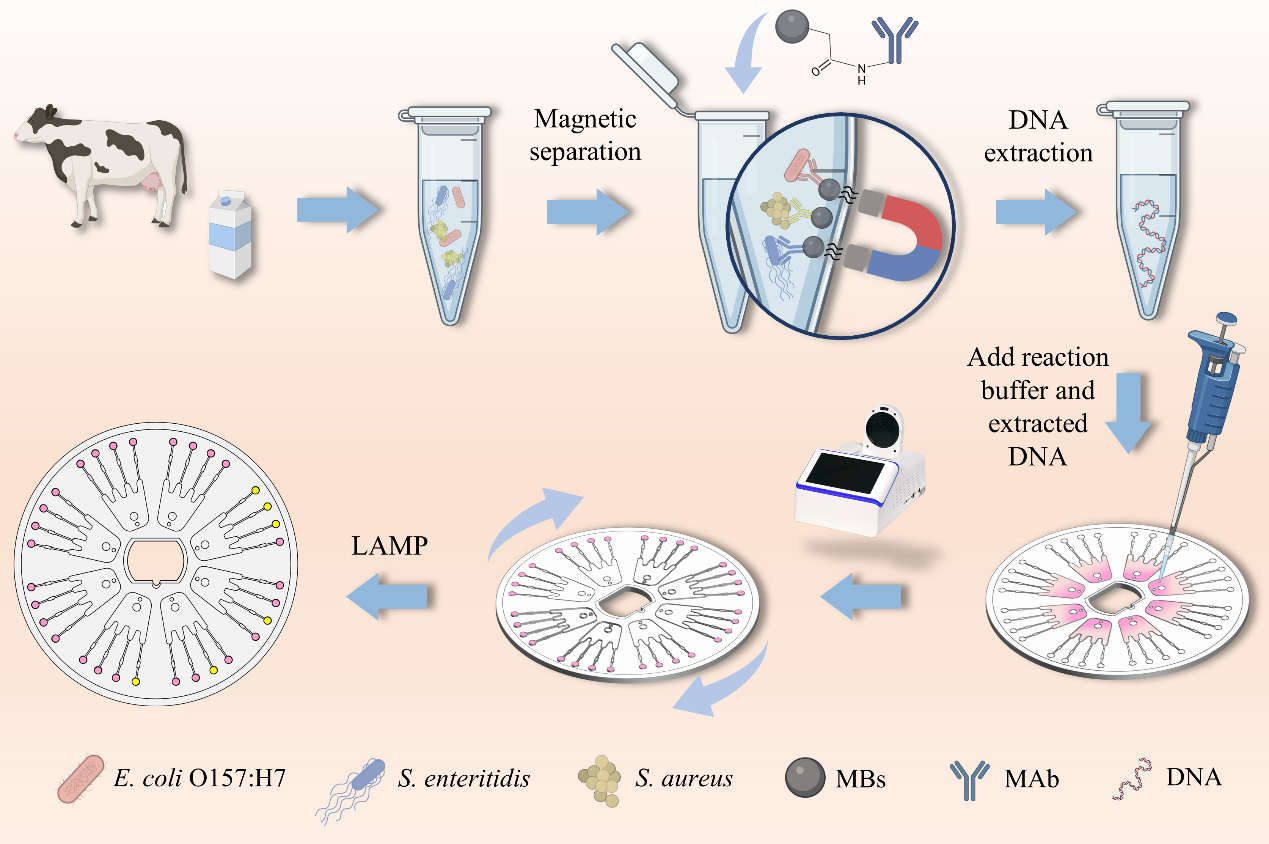
In this study, the authors have constructed a new detection system capable of simultaneously detecting multiple pathogenic bacteria in food, which seamlessly integrates the "one-step reaction in one-tube" sample preparation strategy with microfluidic visualization detection technology. This allows for the enrichment and simultaneous detection of three types of pathogenic bacteria, with the capacity to analyze eight samples concurrently on the microfluidic chip. Moreover, the testing process has been simplified, significantly reducing the time required from bacterial enrichment to the final result to just 80 minutes. Additionally, the detection limit has been lowered to 1.2×102 CFU/mL. In conclusion, the novel system developed in this study demonstrates immense potential for rapid and high-throughput detection of pathogenic bacteria, offering a promising solution for food safety monitoring.
Funding
This work was supported by Shanghai Science and Technology Commission Research Project, Shanghai Natural Science Foundation of China, Shanghai Agriculture Applied Technology Development Program, China, Research Foundation for Advanced Talents of Longyan University, and Basic Foundation for Scientific Research of State-level Public Welfare Institutes of China. Wang Fucheng and Ye Fangyu, master's degree candidates from SHVRI, CAAS, are the co-first authors of this study, and Prof. Jiang Wei and Prof. Han Xiangan are the co-corresponding authors.

