
Recently, National Reference Laboratory for Animal Schistosomiasis of SHVRI preliminarily explored that sja-let-7 could suppress the development of liver fibrosis via Schistosoma japonicum extracellular vesicles ( Sj EVs). Meanwhile, the team also found that the elevated abundance of sja-let-7 in mice alleviate schistosome-induced and carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis. The study provides a new perspective on schistosome-host interactions and new drug candidate molecules for the treatment of liver fibrosis, and the results were published in PloS Pathogens and Biology .
Background
Schistosomiasis is a fatal zoonotic parasitic disease that also threatens human health. The main pathological features of schistosomiasis are granulomatous inflammation and subsequent liver fibrosis, which is a complex, chronic, and progressive disease. EVs derived from schistosome eggs are broadly involved in host-parasite communication and act as important contributors to schistosome-induced liver fibrosis. However, it remains unclear whether substances secreted by the EVs of Schistosoma japonicum , a long-term parasitic “partner” in the hepatic portal vein of the host, also participate in liver fibrosis.
Research Progress
In the present study, the team reported that EVs derived from S. japonicum worms attenuated liver fibrosis by delivering sja-let-7 into hepatic stellate cells. Mechanistically, activation of HSCs was reduced by targeting collagen type I alpha 2 chain and downregulation of the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway both in vivo and in vitro . Meanwhile, the team also found that the elevated abundance of sja-let-7 in mice also alleviate carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis. Overall, these results contribute to further understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying host-parasite interactions and identified the sja-let-7/Col1α2/TGF-β/Smad axis as a potential target for treatment of liver fibrosis.
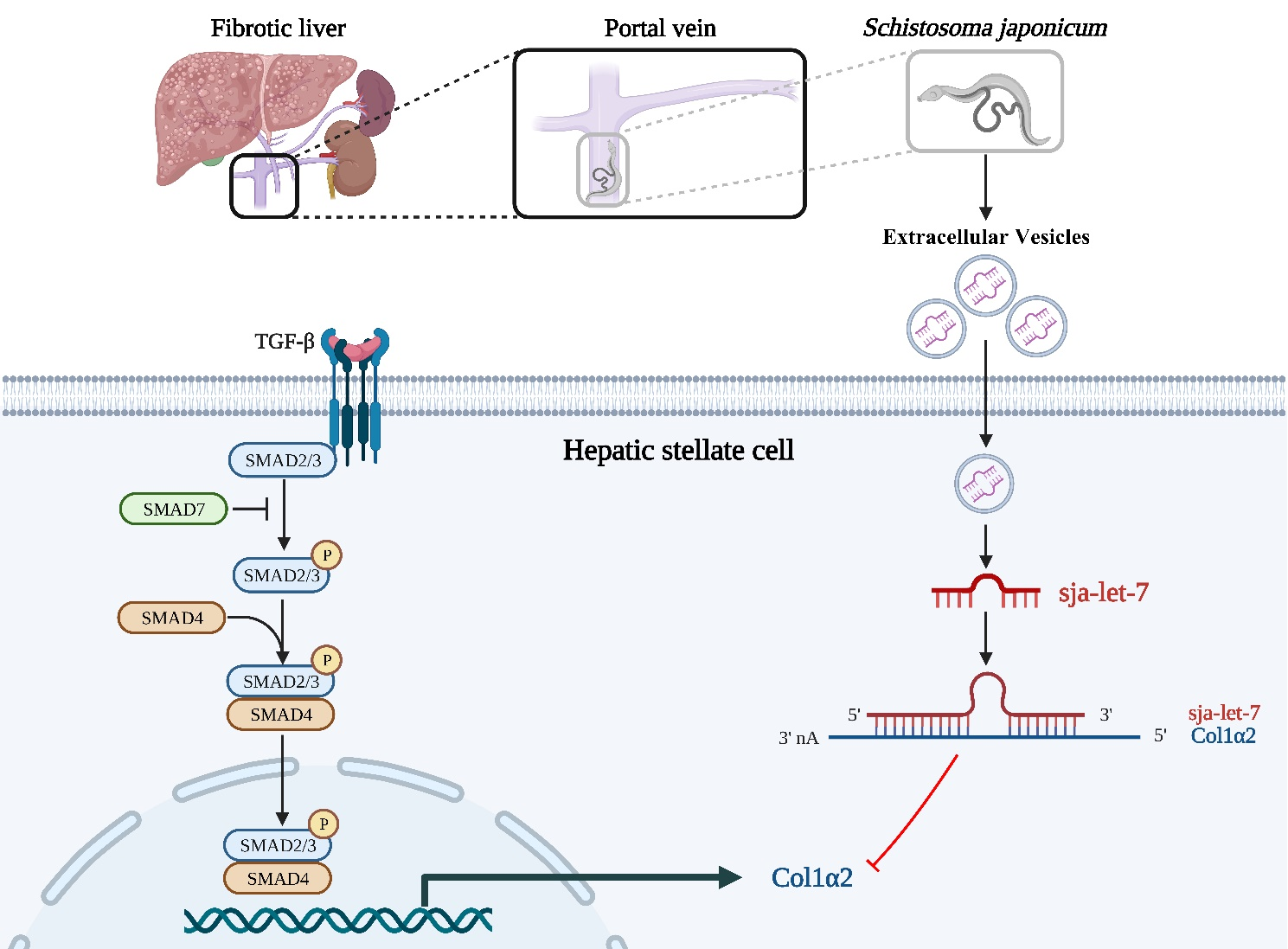
The S. japonicum worms dwelling in the host portal vein release SjEVs that contain sja-let-7 to suppress the schistosome-induced liver fibrosis via Col1α2/TGF-β/Smad axis.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (no.20ZR1469300), the Chinese National Natural Science Foundation (no. 31672245) and the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program (ASTIP) (CAAS-ASTIP-2021-SHVRI). Prof. Yamei Jin from SHVRI, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences was the corresponding author of this article. PhD student Haoran Zhong was the first author.
Link to original article
https://journals.plos.org/plospathogens/article?id="10.1371/journal.ppat.1012153

